Achieving & Maintaining Ideal Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is more challenging than ever in a world where fast food chains outnumber gyms and sugary treats are just a click away. If you’re reading this, chances are, you or someone you love is part of the ever-growing diabetic community. And you’re not alone. Diabetes, specifically Type 2, is on a stark rise, painting a concerning picture of global health.
Blood sugar management is not just a buzzword; it’s a lifeline for those diagnosed with diabetes. Fluctuating glucose levels can play havoc on the body, leading to complications, from fatigue and blurred vision in the short term to more severe consequences like kidney disease, heart problems, and even potential limb amputations in the long run.
As the global diabetic population continues to rise, so does the urgency to understand, manage, and maintain healthy blood sugar levels. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the number of people with diabetes has risen from 108 million to 422 million, with numbers expected to soar in the coming decades. These aren’t just statistics; they’re a loud call to action.
In this guide, we’ll delve deep into the importance of blood sugar management, offering insights, tips, and strategies to help navigate the diabetic journey. Whether you’re newly diagnosed or have been managing diabetes for years, there’s always something new to learn. So, let’s embark on this journey together and prioritize our health in a sugar-dominated world.
Understanding Blood Sugar: The Basics
Diabetes, insulin, glucose – these words often circle in health discussions. But what do they mean, especially in the context of our body’s functions? Let’s break down the basics.
What is Blood Sugar?
Blood sugar, often called glucose, is the primary energy source for our body’s cells. Think of it as the fuel that powers our body’s engine. When we eat, our body breaks down the carbohydrates into glucose. This glucose then enters our bloodstream, ready to be used by our cells for energy. But for this energy transfer to occur, a hormone called insulin, produced by the pancreas, acts as a key, allowing glucose to enter and fuel our cells.
In simple terms, imagine your cells are like little cars. Glucose is the gasoline, and insulin is the nozzle of the gas pump. Without the nozzle (insulin), the gasoline (glucose) can’t get into the car (cell), leaving it powerless.
The Role of Glucose
Now that we’ve established blood sugar let’s discuss its significance. Glucose isn’t just fuel; it’s the preferred energy source for our brain, muscles, and tissues. When our blood sugar levels are balanced, our body functions optimally, and we feel energetic and alert.
However, maintaining healthy glucose levels is a delicate dance. Too much glucose, and we risk conditions like hyperglycemia, which can lead to complications like nerve damage and cardiovascular issues. Too little glucose, termed hypoglycemia, deprives our body of its primary energy source, leading to dizziness, confusion, and, in severe cases, even unconsciousness.
Striking the right balance is crucial. For people with diabetes, where the body’s natural mechanism of regulating blood sugar is compromised, understanding and actively managing glucose levels becomes a pivotal aspect of daily life.
In the following sections, we’ll explore the consequences of uncontrolled blood sugar and how one can effectively manage and maintain it within healthy ranges.
The Impact of Uncontrolled Blood Sugar
Our system’s delicate blood sugar balance is akin to walking a tightrope. Lean too much to one side, and you risk falling. Similarly, veering too far from optimal blood sugar levels can lead to a cascade of health issues. While some effects are immediate and short-lived, others, when unchecked, can have lasting and irreversible consequences.
Short-term Effects
Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
It’s called hypoglycemia when blood sugar levels drop below the normal range. It can happen for various reasons, including skipping meals, taking too much diabetes medication, or engaging in sudden, intense physical activity. The body reacts almost instantly:
- Symptoms are dizziness, trembling, sweating, hunger, irritability, and confusion.
- Severe cases are seizures, unconsciousness, and, in rare situations, death.
- Management: Immediate consumption of fast-acting carbohydrates like fruit juice or candy will raise blood sugar levels quickly.
Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar)
On the other end of the spectrum is hyperglycemia, where blood sugar levels are too high. Causes can range from consuming high-carbohydrate meals, stress, or not taking enough diabetes medication.
- Symptoms are frequent urination, excessive thirst, fatigue, blurred vision, and headache.
- In severe cases, there is diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), where the body starts breaking down fats too quickly, leading to a buildup of ketones in the bloodstream. It is a medical emergency.
- Management: Adjusting medication, drinking water to flush out excess sugar through urine, and monitoring blood sugar levels closely.
Long-term Consequences
Chronic uncontrolled blood sugar doesn’t just have an immediate toll on the body; its effects are profound and long-lasting.
Neuropathy (Nerve Damage)
High blood sugar can damage nerves throughout the body, but it’s most common in the legs and feet. It can lead to:
- Tingling, pain, or numbness in the extremities.
- Onset of sharp, jabbing pain that may be worse at night.
- Extreme sensitivity to touch.
Retinopathy (Eye Damage)
Diabetes can lead to eye problems, the most severe being diabetic retinopathy, which can result in blindness.
- Early stages might have no symptoms.
- Over time, it can cause blurry vision, floaters, and vision loss.
Other Complications
- Cardiovascular problems: heart attack, stroke, and narrowing of arteries.
- Kidney Damage: Diabetes can impair the kidneys’ filtering system, leading to kidney failure.
- Foot Issues: Nerve damage and poor blood flow can lead to serious foot complications.
The picture painted by uncontrolled blood sugar is grim, but it’s not all doom and gloom. With proactive management, regular check-ups, and lifestyle modifications, it’s possible to keep these complications at bay. The key is understanding the risks and taking active measures to mitigate them.
The pie chart visualizes “The Impact of Uncontrolled Blood Sugar.” The chart segments showcase various effects and complications due to unregulated blood sugar levels. Remember that the segment sizes are approximated for visual representation and do not represent precise statistical data.
Tools to Monitor Blood Sugar
In the battle against diabetes, knowledge is power. And this knowledge comes from accurate, timely monitoring of blood sugar levels. Over the years, technological advancements have brought forth a range of tools to aid people with diabetes in tracking their glucose levels. Two of the most prominent tools in today’s landscape are traditional glucose meters and Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs). Let’s dive deeper into their functionalities and understand their pros and cons.
Traditional Glucose Meters
These are the handheld devices that have been around for decades and are widely used by diabetics around the world.
Functionality:
- A small blood sample, usually obtained by pricking the fingertip with a lancet, is placed on a test strip that the meter reads.
- The meter displays the blood sugar level on a digital screen within seconds.
Reliability:
- Generally accurate, provided the meter is calibrated correctly, and the test strips are not expired.
- Keeping the device clean and following the manufacturer’s instructions is essential for accurate results.
Pros:
- Portable and easy to use.
- It is affordable for most users, with many insurance plans covering the cost.
Cons:
- Requires regular finger pricks, which can be painful.
- Can only provide glucose readings at the specific moment of testing.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
These are relatively newer innovations and offer real-time tracking of blood sugar levels.
Functionality:
- A sensor is inserted under the skin (usually on the abdomen or arm), which measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid.
- This sensor continuously sends data to a device that displays real-time glucose readings.
Benefits:
- Provides insights into glucose trends, showing how levels rise or fall over time.
- Reduces the need for finger pricks.
- Alarms can be set to alert the user if glucose levels go too high or too low.
- Some models can integrate with insulin pumps for more coordinated care.
Challenges:
- They are more expensive than traditional meters. While prices are dropping, they may not be covered by all insurance plans.
- Depending on the model, The sensor must be replaced every 7-14 days.
- While it reduces the need for finger pricks, occasional calibration with a traditional meter might be required.
With these tools, people with diabetes today are better equipped to manage their condition. Choosing between a traditional glucose meter and a CGM will depend on individual needs, lifestyle, and financial considerations. The key is consistent monitoring, understanding the data, and making informed decisions in collaboration with healthcare professionals.
Natural Ways to Balance Blood Sugar
While medications are essential in managing diabetes, lifestyle choices significantly influence blood sugar levels. Embracing natural methods can help stabilize glucose and enhance overall well-being. From the foods we eat to our physical activity and even our mental state, every aspect plays a role in the diabetic journey.
Dietary Choices
Food is fuel, but for diabetics, it’s also a tool for maintaining balanced blood sugar levels.
Carbohydrates:
- It has the most impact on blood sugar. Once ingested, it breaks down into glucose.
- Not all carbs are created equal. Complex carbs (like whole grains and vegetables) release sugar slowly, ensuring steady glucose levels, while simple carbs (like candies and sodas) can cause rapid spikes.
Proteins:
- Protein doesn’t impact blood sugar levels as directly as carbs. However, it helps in feeling full and stabilizing blood sugar.
- Choosing lean proteins like chicken, fish, tofu, and beans is essential.
Fats:
- Healthy fats can slow sugar absorption, helping stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Focus on sources like avocados, nuts, olive oil, and fatty fish.
Superfoods for Diabetics:
- Berries: Packed with antioxidants and fiber, they offer sweetness without spiking blood sugar.
- Leafy Greens: Low in calories and carbs but high in nutrients.
- Nuts: Rich in fiber and healthy fats, they help stabilize blood sugar.
- Chia Seeds can help manage glucose levels.
- Beans: A good source of protein and fiber, they have a low glycemic index.
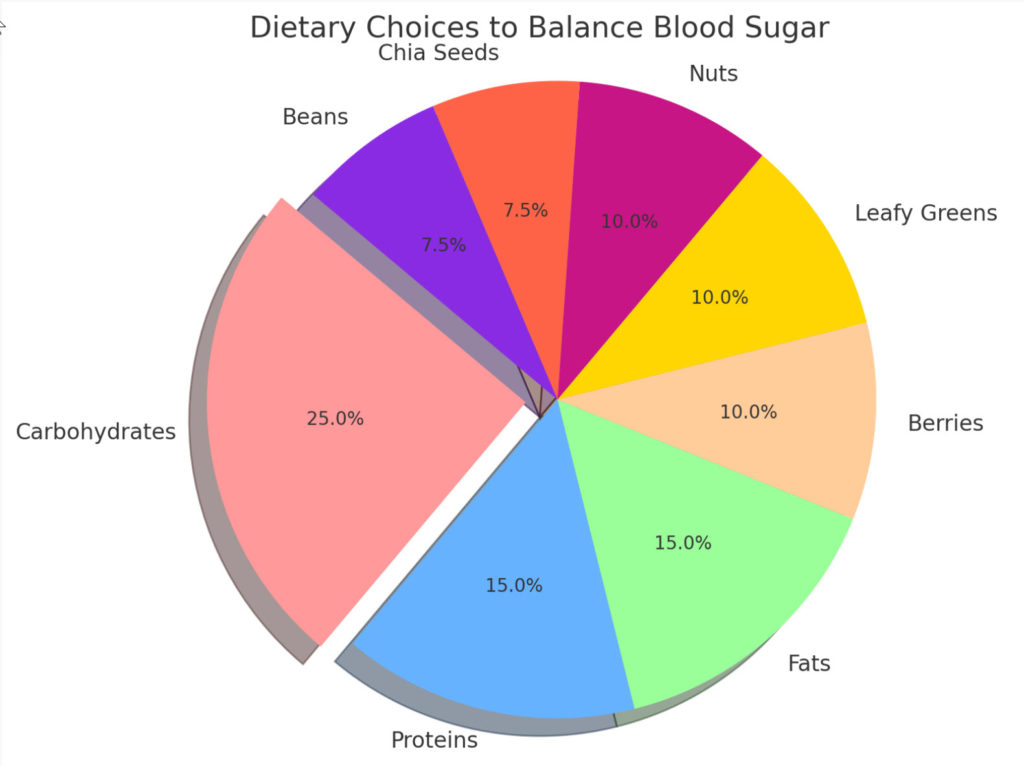
The pie chart visualizes “Dietary Choices to Balance Blood Sugar.” The chart segments showcase the various dietary components and their approximated significance in managing blood sugar levels. Remember that these segment sizes are for visual representation and do not represent precise statistical data.
The Exercise Factor
Physical activity is helpful for diabetes management, offering a natural way to lower and regulate blood sugar levels.
Importance:
- Exercise helps muscles use up glucose, reducing blood sugar in the process.
- Regular physical activity enhances insulin sensitivity.
Best Exercises for Diabetics:
- Walking: A simple yet effective way to regulate blood sugar.
- Swimming: Offers a full-body workout without stressing the joints.
- Cycling: This can be done outdoors or on a stationary bike.
- Yoga: Helps in relaxation, flexibility, and muscle toning.
- Strength Training: Lifting weights helps build muscle, improving blood sugar control.
Stress and Blood Sugar
The mind-body connection plays a pivotal role in diabetes management. Chronic stress can significantly affect glucose levels.
The Connection:
- When stressed, the body raises blood sugar levels.
- Chronic stress, whether from work, personal issues, or even the daily management of diabetes, can keep blood sugar elevated.
Stress-Management Techniques:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Helps in grounding thoughts and reducing anxiety.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Offers immediate relaxation and lowers cortisol levels.
- Physical Activity: As mentioned, exercises like walking or yoga can double up as stress relievers.
- Hobbies: Engaging in reading, painting, or gardening can divert the mind and reduce stress.
Incorporating these natural methods doesn’t just offer better blood sugar control but paves the way for a healthier, more fulfilling life. While these strategies are beneficial, they should complement medical treatments and be discussed with healthcare professionals to ensure holistic diabetes care.
Navigating Medications & Supplements
For many living with diabetes, medications and supplements are a daily reality. They play a pivotal role in managing blood sugar levels and preventing complications. But with many options available, it’s essential to understand their functions, benefits, and potential side effects. Let’s dive deep into the world of diabetic medications and natural supplements.
The Insulin Guide
People with diabetes either don’t produce enough insulin or can’t effectively use the insulin they produce.
Different Types:
- Rapid-Acting Insulin: Starts to work shortly after injection and peaks in about an hour. It continues to work for two to four hours. Examples include Lispro (Humalog) and Aspart (NovoLog).
- Short-Acting Insulin: Starts to work within a half hour after injection and peaks in two to three hours. It continues to work for three to six hours. An example is Regular or R insulin.
- Intermediate-Acting Insulin: Starts to work about two to four hours after injection and peaks four to 12 hours later. It remains effective for up to 18 hours. Examples include NPH (Humulin N, Novolin N).
- Long-Acting Insulin: Works for nearly 24 hours. Examples are Glargine (Lantus) and Detemir (Levemir).
Usage:
- Insulin can’t be taken orally as stomach enzymes interfere with its action. It’s administered through injections or insulin pumps.
- The type and dosage of insulin are tailored to each individual based on their blood sugar levels, lifestyle, and specific diabetes type.
Oral Medications
While insulin is a mainstay treatment for Type 1 diabetes, several oral medications can help manage Type 2 diabetes.
- Metformin (Glucophage, Glumetza): This is often the first medication prescribed. It improves the sensitivity of body tissues to insulin.
- Sulfonylureas: These medications help your body secrete more insulin.
- Thiazolidinediones: Like metformin, these drugs make the body’s tissues more sensitive to insulin. Examples are rosiglitazone (Avandia) and pioglitazone (Actos).
- DPP-4 inhibitors: These moderate blood sugar levels by impacting the behavior of pancreatic and liver enzymes. Examples include sitagliptin (Januvia) and linagliptin (Tradjenta).
Natural Supplements for Blood Sugar Control
Nature offers several remedies that can aid in blood sugar management. While they shouldn’t replace prescribed medications, they can complement them.
- Cinnamon: Studies suggest that cinnamon can improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels.
- Fenugreek: Rich in soluble fiber, fenugreek seeds can help control blood sugar by slowing down carbohydrate digestion and absorption.
- Berberine: Traditionally used in Chinese medicine, berberine has been shown to help regulate blood sugar and improve insulin function.
Note: Before starting any supplement, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional. Some natural supplements can interact with medications or have side effects.
The world of diabetes medications and supplements is vast and continually evolving. It’s crucial to stay informed and collaborate with healthcare providers to find the best regimen for individual needs. Regular monitoring and adjustments ensure optimal blood sugar control and a healthier life.
Routine Check-ups: A Diabetic’s Best Friend
Living with diabetes is akin to walking a tightrope—balance is essential, and consistent monitoring is the safety net. While daily blood sugar tracking at home offers a snapshot of one’s condition, routine check-ups with healthcare professionals provide a broader, more comprehensive view. These visits are not just about numbers but about understanding, adjusting, and preempting potential health challenges.
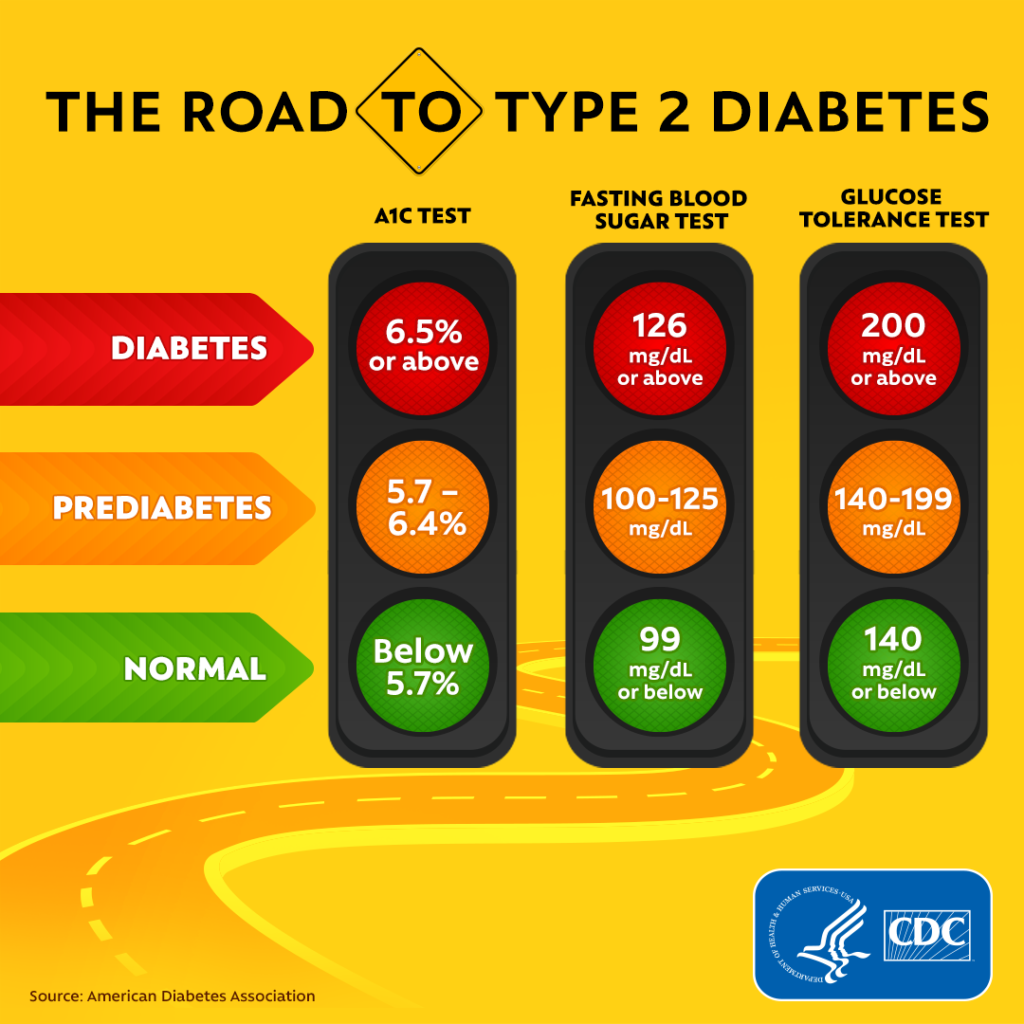
The A1C Test Decoded
The A1C test is a cornerstone in diabetes management. Unlike daily glucose tests, which provide immediate but transient blood sugar levels, the A1C test offers a longer-term view.
Monitoring Average Blood Sugar:
- The A1C measures the percentage of blood sugar.
- It provides an average blood sugar over the past two to three months.
- The higher the A1C level, the poorer the blood sugar control, implying a higher risk of diabetes complications.
- For most diabetics, an A1C level below 7% is a common treatment target, but this can vary based on individual health profiles.
Help Manage Your Diabetes With Remarkable Accuracy
Importance:
- It helps assess the effectiveness of the current treatment plan.
- Can indicate if adjustments in medications or lifestyle changes are needed.
- Reduces the reliance on daily blood sugar tests to gauge overall diabetes control.
The Power of Regular Doctor Visits
While the A1C test is crucial, it’s just one piece of the puzzle. Regular consultations with healthcare professionals offer a holistic approach to diabetes management.
Early Detection:
- Routine examinations can detect signs of potential complications early, such as retinopathy (eye damage), neuropathy (nerve damage), or cardiovascular issues.
- Urine tests can assess kidney function, and blood pressure measurements can indicate cardiovascular health.
Prevention of Complications:
- Doctors can recommend preventive measures based on regular check-ups, such as dietary changes, exercise regimens, or medication adjustments.
- These visits allow patients to discuss any concerns, symptoms, or challenges, ensuring they receive timely advice and interventions.
Education & Support:
- Healthcare professionals can provide updates on the latest diabetes research, new medications, or tools.
- They can also offer psychological support, connecting patients with therapists, counselors, or support groups to address the emotional challenges of living with diabetes.
For a diabetic, routine check-ups are not just appointments on a calendar; they’re lifelines. They offer a roadmap, guiding patients through the challenges of diabetes, ensuring they’re surviving and thriving. Regular visits and proactive self-management lay the foundation for a healthier, more fulfilling life with diabetes.
Personal Triumphs Over Diabetes
Every individual diagnosed with diabetes has a unique journey. While the medical charts and numbers paint a clinical picture, the real stories lie in personal experiences, struggles, and triumphs. These tales of resilience, determination, and adaptability inspire countless others on a similar path. Let’s delve into two such stories of hope and success.
John’s Transformational Journey
John, a 45-year-old accountant, had always been the life of the party. But a routine check-up brought forth a diagnosis that would change his life: Type 2 Diabetes. The initial shock was palpable. His love for sugary treats and a sedentary lifestyle had caught up with him.
Acceptance: The first few weeks were filled with denial. John believed it was just a minor hiccup. But as reality sank in, he realized acceptance wasn’t a sign of defeat. It was the first step towards positive change.
Successful Management:
- Education: John delved deep, reading up on diabetes, attending workshops, and joining support groups.
- Dietary Changes: Gone were the days of impulsive eating. In came balanced meals, portion control, and a keen eye on nutrition labels.
- Physical Activity: John discovered a love for morning walks, which soon progressed to jogging. The weekends saw him cycling or hiking.
Today, three years post-diagnosis, John’s A1C levels have consistently remained in the desired range. His energy levels are higher than ever, and his life perspective has transformed. Diabetes wasn’t just a condition for John but a catalyst for a healthier, more conscious lifestyle.
Maria’s Dietary Revolution
Maria, a 32-year-old software engineer, was diagnosed with Gestational Diabetes during pregnancy. Post-delivery, while her baby was healthy, Maria’s blood sugar levels remained a concern.
The Challenge: Juggling a newborn, a demanding job, and erratic blood sugar levels were overwhelming. Maria often resorted to fast food and ready-to-eat meals, leading to weight gain and worsening blood sugar control.
Informed Choices: A visit to a nutritionist was Maria’s turning point. She learned the profound impact of food choices on her well-being.
- Meal Planning: Maria began planning her meals, ensuring a balance of protein, healthy fats, and complex carbs.
- Superfoods: She incorporated diabetic-friendly superfoods like chia seeds, berries, and leafy greens.
- Mindful Eating: Instead of eating in front of her computer, Maria practiced mindful eating, savoring each bite and listening to her body’s hunger cues.
A year into her dietary revolution, Maria’s blood sugar stabilized, and she also shed the extra weight and felt more energetic and focused. Her relationship with food had transformed from one of convenience to one of nourishment and care.
John’s and Maria’s stories are but two among millions. They serve as a testament that while diabetes is a life-altering diagnosis, it doesn’t define one’s life. With determination, knowledge, and the proper support, triumphs are not just possible; they’re inevitable.
Everyday Tips for Diabetics
Living with diabetes requires more than just periodic check-ups and medications. The daily habits, the small choices, and the nuances of everyday life can significantly impact blood sugar management. Let’s explore some simple tips that can make a difference for those navigating life with diabetes.
Reading Food Labels
Understanding what’s in our food is vital in processed foods.
Making the Right Food Choices:
- Total Carbohydrates: This is the most crucial part of the label for people with diabetes. Remember, it’s not just about sugars but also fibers and starches.
- Serving Size: Always check the serving size. A product might seem low in carbs, but the serving size could be tiny.
- Ingredients List: are listed in descending order by weight. Be cautious if sugar or its variants (like high fructose corn syrup) are listed among the first few ingredients.
- Sugar Alcohols: Often used in “sugar-free” products, they can still impact blood sugar levels, though typically less than regular sugar.
- Fats: Opt for products low in saturated and trans fats. Look for higher monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
Traveling with Diabetes
Hitting the road or taking to the skies requires more preparation for someone with diabetes.
Preparations for Hassle-free Journeys:
- Medication Stock: Always carry more medication and supplies than you need. Delays are unpredictable.
- Keep Medications Accessible: If flying, always keep your medications and glucose monitoring equipment in your carry-on.
- Time Zones: If traveling across time zones, consult your doctor about adjusting medication schedules.
- Snacks: Carry a stash of diabetic-friendly snacks to avoid low blood sugar episodes.
- Stay Hydrated: Travel, especially air travel, can be dehydrating. Drink plenty of water.
- Identification: Wear a medical ID that states you have diabetes.
Curbing Sugar Cravings
Sugar cravings can be a formidable foe for people with diabetes. But with a bit of strategy, they can be managed.
Healthy Alternatives:
- Fruit: Opt for fruits like berries or apples when craving something sweet. They offer natural sugars along with beneficial fibers and antioxidants.
- Dark Chocolate: In moderation, dark chocolate (70% cocoa or more) can be a healthier alternative to sugary treats.
- Yogurt: Unsweetened Greek yogurt can satisfy sugar cravings while providing beneficial proteins.
Strategies:
- Mindful Eating: Slow down when eating and enjoy each bite.
- Stay Full: Ensure your meals have a good balance of protein, fats, and fibers. It can prevent blood sugar drops, which can trigger sugar cravings.
- Hydration: Sometimes, our bodies confuse thirst with hunger or sugar cravings. Drink water first and see if the urge subsides.
Navigating everyday life with diabetes doesn’t have to be daunting. With a few tweaks, some preparation, and an informed approach, managing diabetes can seamlessly integrate into daily routines, paving the way for a healthier, more fulfilling life.
Conclusion
Blood sugar control is not just a clinical recommendation; it’s the cornerstone of well-being for those with diabetes. Like the intricate gears in a clock, every aspect of our lives—from the food we eat the activities we engage in, to the thoughts we harbor—plays a role in this balance. And while the journey might seem daunting, it’s essential to remember that it’s a marathon, not a sprint.
Navigating the complexities of diabetes is undeniably challenging. There will be highs and lows, both in terms of blood sugar readings and emotional journeys. But every hurdle overcome, every informed food choice, and every extra step walked is a testament to resilience and determination.
The significance of blood sugar control extends beyond numbers on a glucometer. It’s about embracing a quality of life, savoring moments without the looming shadow of complications, and forging ahead with confidence and knowledge.
To every individual managing diabetes: Your efforts are monumental, no matter how small they seem. Every positive step you take every challenge you face head-on, adds up, creating a ripple effect of positive change in your health journey. The path to optimal blood sugar control is paved with persistence, knowledge, and the undying spirit to thrive. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; every positive step truly counts. Stay empowered, stay informed, and keep shining!
Join Our Community!
Engage with Us: Your journey, insights, and experiences are invaluable. Dive into our community and share your stories or tips in the comments below. Whether you’ve found a fantastic diabetic-friendly recipe or have a tale of triumph, we want to hear from you. Your insights could be the beacon of hope or wisdom someone else needs.
Stay Updated: Knowledge is power, especially when managing diabetes. Sign up for our diabetic-friendly newsletter and stay abreast of the latest research, recipes, and lifestyle tips tailored for you. Let’s journey towards better health, one informed step at a time.
We can create a thriving community that supports, educates, and uplifts. Let’s transform challenges into opportunities and pave the way for a healthier tomorrow!
Introducing GlucoTrust, a cutting-edge supplement proudly made in the USA. Harnessing the power of all-natural ingredients, GlucoTrust supports healthy blood sugar management, sustainable weight loss, and restful sleep, all in one safe and effective formula.
Try My Healthy Meal Planner
Transform your meal planning with our Healthy Meal Planner GPT! This personalized tool helps you create balanced, organic meal plans tailored to your dietary needs and nutritional goals. Enjoy delicious recipe suggestions, easy grocery lists, and tips for efficient meal prep. Stay motivated and on track with our supportive, friendly guidance. Start your journey to a healthier you today!